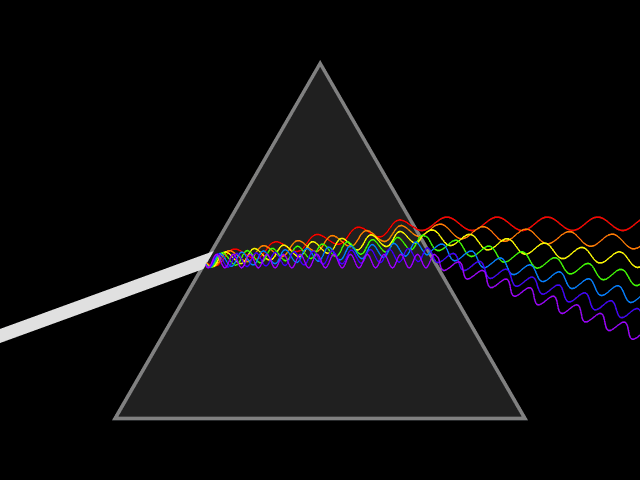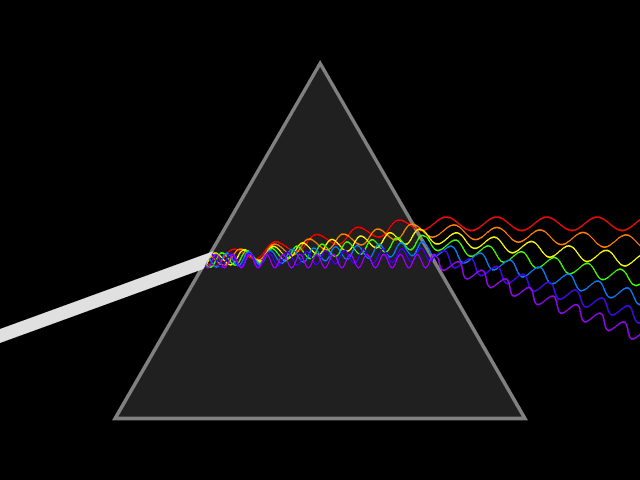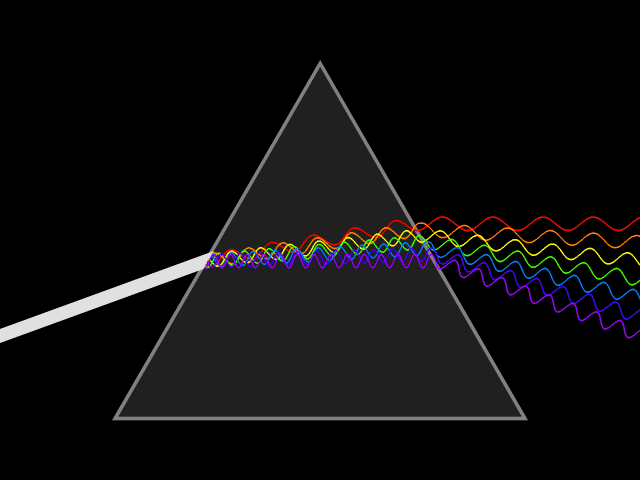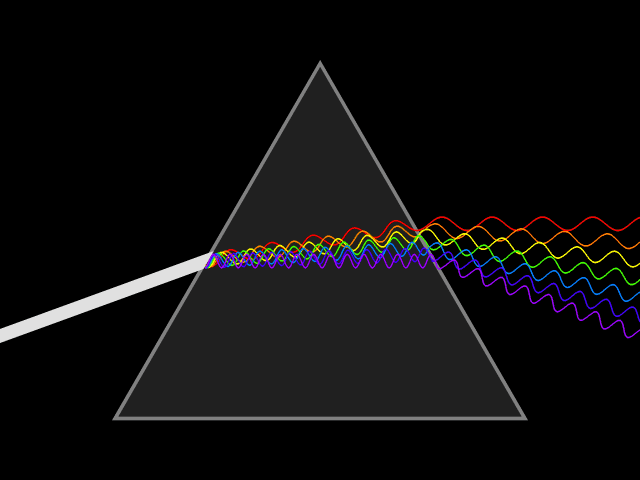
Waves are super popular mechanism for energy to travel through the universe. Light, sound and earthquake energy all travel in wave patterns through matter. Let’s learn some basic vocabulary we use to discuss the characteristics of waves
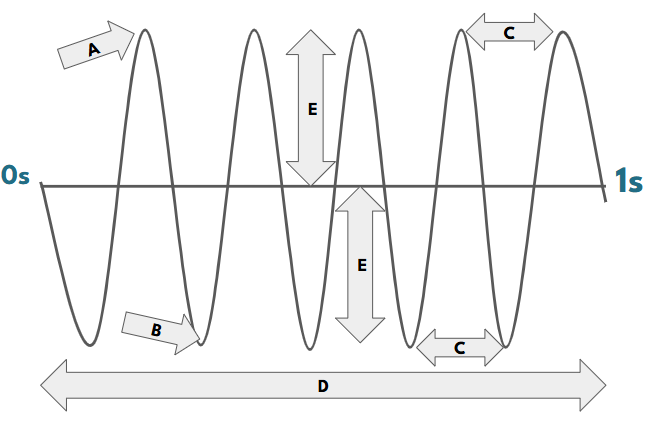
Our basic mathematical representation of a wave is in repeating “S”-like pattern as shown below. And while there are more variations to learn about, let’s start with understanding this model:
- PEAK (A) is the top of the wave.
- TROUGH (B) is the bottom of the wave.
- WAVELENGTH (C) is the distance from peak-to-peak or trough-to-trough.
- Wavelengths can range from fractions of a millimeter to miles.
- FREQUENCY (D) is the number of waves that take place in 1 second and is measured in HERTZ.
- AMPLITUDE (E) is the height of the wave from the center to the peak or center to the trough.
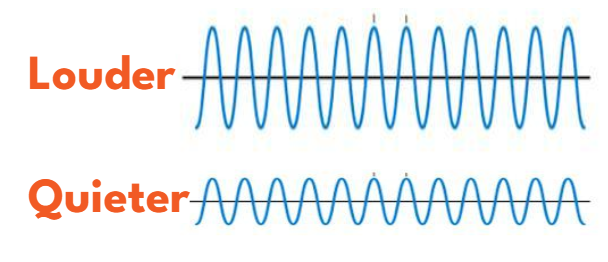
The AMPLITUDE (or height) of a sound wave determines the volume of a sound, which is measured in DECIBELS.
- Higher amplitudes create louder sounds.
- Lower amplitudes result in quieter sounds.
- Just as taller waves at the beach make a louder crashing sound, the height of the louder wave is taller than the quieter one below.
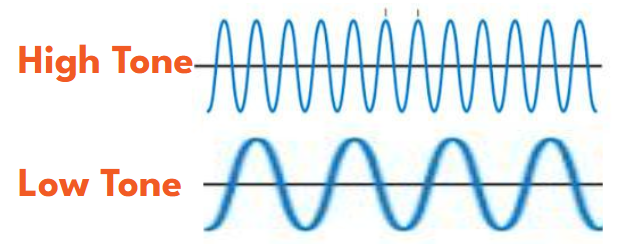
The FREQUENCY (number of waves in a second) of a sound wave determines the tone or pitch of the sound, which is measured in HERTZ.
- Higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths and make a high pitch sound.
- Lower frequency waves have longer wavelengths and make a low pitch sound.
- Check out this website to see what different Hertz sound like.
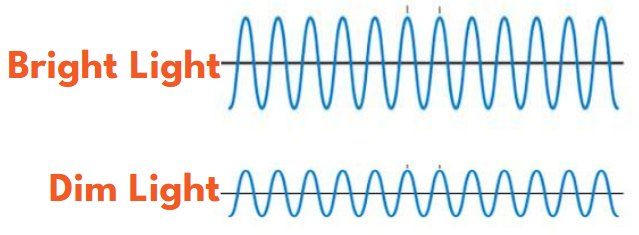
The AMPLITUDE of a light wave determines the brightness of the light and is measured in Lux or Lumens.
- Light photons vibrating in taller waves create brighter light regardless of the color.
- Those vibrating in shorter height waves create dimmer light.
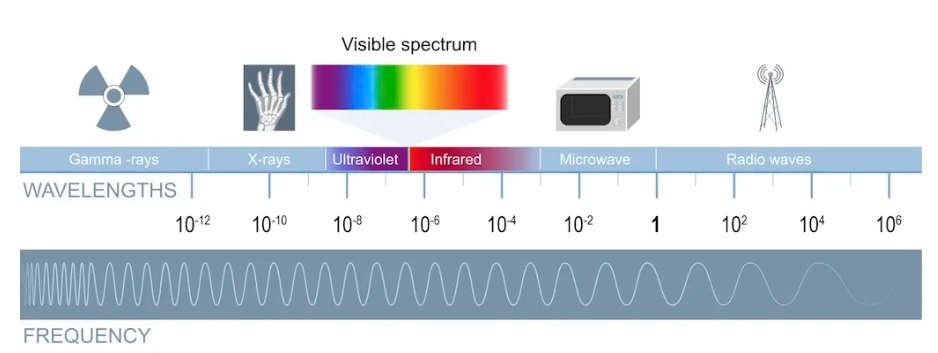
- Because light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, the scale of low to high frequency gets a little more complicated.
- However, in terms of visible light, the Terahertz (THz) determines the color ranging from lower frequency violet to higher frequency red.
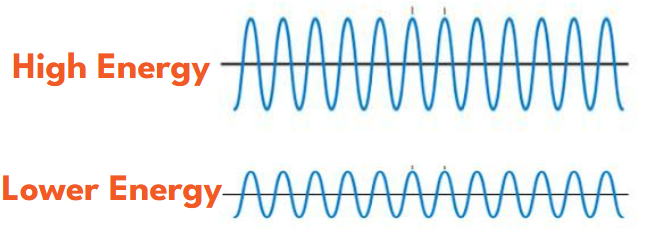
Since all waves are the same, imagine you’re a the beach and small waves are lapping at the shore. Then along comes a much taller wave that knocks you over.
- This higher amplitude wave carries more energy which is true of louder sounds and brighter lights too!
- Lower amplitude waves, like small ripples in a glass of water, quiet sounds and dimmer light, carry less energy and are less likely to damage human cells.
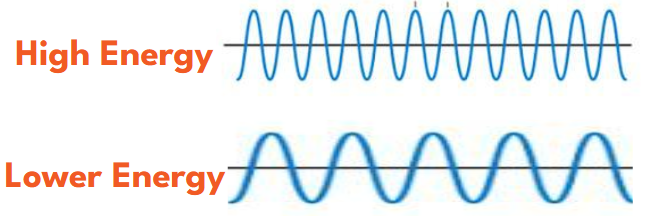
Keeping our beach scenario in mind, if you get hit by one wave vs many waves coming very quickly, you will easily feel the added energy from the added waves.
- These higher frequency waves carry more energy which is true of higher pitch sounds and gamma rays which can damage human cells.
- Lower frequency waves, like an occasional wave at the beach, lower pitch sounds and radio wave, carry less energy and are less likely to cause damage.
What’s next?
I’m lost😱
Since this is lesson 1 of the WAVES unit, the only going back is to the Start Page…
I need practice 🤔
I think I get it, but would like some more practice!
Let’s move on👍
I’ve got Wave Properties under control, Let’s learn how they interact with the universe!